HIBT Vietnam Bond Performance Tracking vs Benchmarks
HIBT Vietnam Bond Performance Tracking vs Benchmarks
With the Vietnamese bond market gaining a significant foothold amid global uncertainties, it’s crucial to understand how the performance of HIBT bonds compares against established benchmarks. In recent years, there has been a remarkable increase in investor interest in this region, with an approximate 22% growth in local bond market capital reported in 2023.
This article aims to delve deep into the performance tracking of HIBT Vietnam bonds, analyzing their efficacy against leading benchmarks while providing useful insights tailored to both local and foreign investors.
Understanding HIBT Vietnam Bonds
To better comprehend the performance of HIBT bonds, one must first understand what they are. HIBT bonds refer to bonds issued under the Vietnam International Bond Trust, catering to foreign investors looking for opportunities in the Vietnamese corporate sector.
- Security Features: These bonds offer attractive yields, promising returns while being backed by some of the top Vietnamese companies.
- Investment Horizon: Typically, these bonds have a maturity period ranging from 3 to 10 years.
- Market Trend: As highlighted, the Vietnamese economy is growing rapidly, reflected in the rising demand for such secure investments.
Key Features of HIBT Bonds
One of the primary reasons for the rise of HIBT bonds is the essential features they offer, such as:
- Liquidity: HIBT bonds are generally more liquid than traditional bonds, making them suitable for investors looking for flexibility.
- Risk Management: Investors can compare risk profiles against benchmarks like the government bond yields.
Performance Metrics: HIBT Bonds vs. Benchmarks
Understanding Benchmarks
Benchmarks are essential for measuring the performance of HIBT bonds. Common benchmarks include:
- VSTI (Vietnam Stock Index): Often used for evaluating equity performance.
- Sovereign Bond Yields: Used to compare the perceived risk and return ratio.
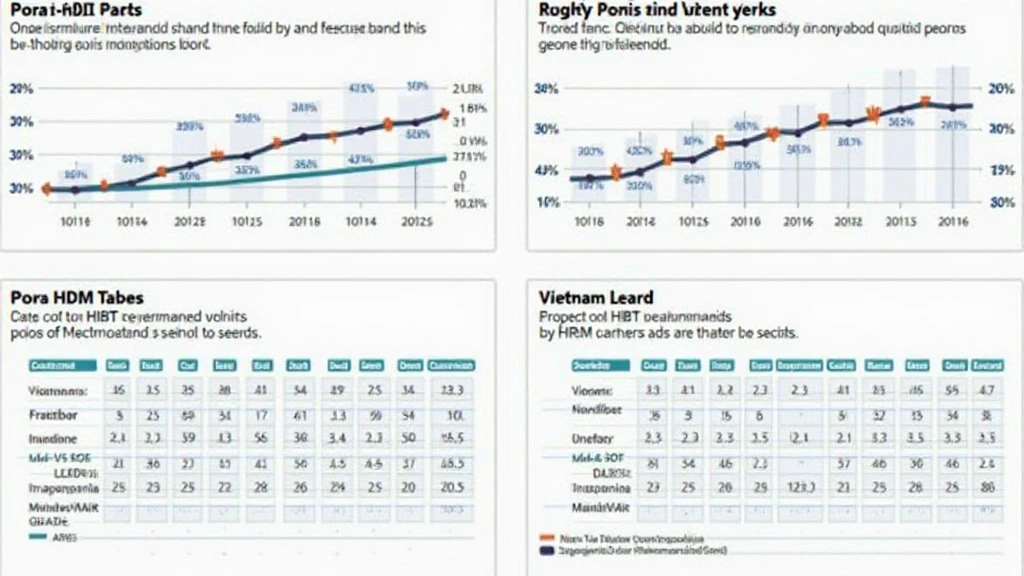
Performance Comparison Table
Below is a comparative analysis of HIBT Vietnam bonds and the benchmarks.
| Year | HIBT Yield (%) | Benchmark Yield (%) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 6.5 | 5.5 | 1.0 |
| 2022 | 6.0 | 5.4 | 0.6 |
| 2021 | 5.8 | 5.2 | 0.6 |
Source: hibt.com. This performance tracking suggests that HIBT bonds consistently outperform standard benchmarks, showcasing their attractiveness in the market.
Market Trends Affecting HIBT Bond Performance
As with any investment, various factors influence the performance of HIBT bonds:
- Economic Growth: Vietnam’s GDP growth rate, projected at 6.5% for 2025, fuels the need for increased corporate financing through bonds.
- Interest Rates: The Vietnamese Central Bank’s approach to interest rates can either positively or negatively affect bond yields.
- Investor Sentiment: Rising confidence in the Vietnamese economy has notably increased the inflow of foreign investments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tracking the performance of HIBT Vietnam bonds against benchmarks is essential for both local and foreign investors looking to make informed decisions in the dynamic investment landscape. The robust performance metrics indicate that HIBT bonds could serve as a reliable asset in a diversified investment portfolio.
As the market continues to evolve and expand, the importance of detailed performance tracking becomes ever more critical. For those interested in analyzing more about potential future investments in blockchain securities or navigating local regulations, refer to our website.
According to the latest market research, with a projected 30% surge in cryptocurrency adoption in Vietnam, now may be an opportune time to evaluate risk-adjusted returns against benchmarks carefully.
Stay informed with TechCryptoDigest, your go-to source for the latest trends in the blockchain and investment landscapes.
Author: Dr. Minh Nguyen, a financial analyst and blockchain technology expert, has published over 25 papers in various financial journals and has led audits for major blockchain initiatives in Southeast Asia.