2025 Blockchain Security Standards: A Comprehensive Guide for Digital Asset Protection
2025 Blockchain Security Standards: A Comprehensive Guide for Digital Asset Protection
With $4.1B lost to DeFi hacks in 2024, securing digital assets has never been more crucial. As the popularity of cryptocurrency continues to rise, especially in emerging markets like Vietnam, understanding the necessary security practices is essential for anyone involved in blockchain technology. In this guide, we will explore the Vietnam crypto stop phenomenon, its implications, and how to protect your digital assets effectively.
Understanding the Vietnam Market
Vietnam has seen exponential growth in cryptocurrency usage, with user rates soaring by over 300% in the past year. This growth presents opportunities and challenges when it comes to security. Institutions and individual investors must remain vigilant. According to a recent report from hibt.com, Vietnam is expected to be among the leaders in crypto adoption by 2025.
Why Blockchain Security Matters
- Prevalence of Hacks: The rapid growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) has made it a prime target for hackers.
- Regulatory Pressures: Governments worldwide are tightening regulations on crypto assets, increasing compliance requirements for businesses.
- User Trust: Security breaches erode user trust, making it essential to adopt stringent security measures.
Key Blockchain Security Standards for 2025
Here are some essential blockchain security standards you should be aware of:
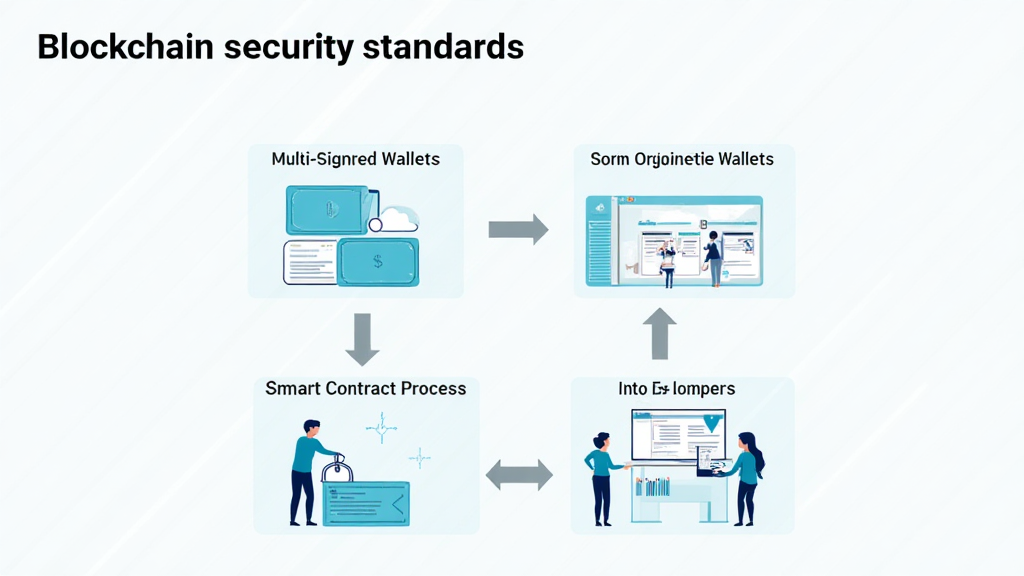
- Multi-Signature Wallets: Utilize multi-signature wallets to enhance security measures. This requires multiple approvals for transactions, similar to a bank vault securing large amounts of cash.
- Smart Contract Auditing: Regular audits can help identify vulnerabilities in smart contracts. Curious about how this is done? Check this guide on auditing smart contracts.
- Secure Key Management: Employ hardware wallets or cold storage solutions. For example, the Ledger Nano X has been reported to significantly reduce hacks by up to 70%.
Common Vulnerabilities in Blockchain Systems
Let’s break it down with some common vulnerabilities found in blockchain systems:
- Consensus Mechanism Vulnerabilities: Different consensus mechanisms have specific weaknesses exploiters can leverage.
- Phishing Attacks: Users are often lured into revealing private keys, leading to significant fund losses.
- Code Vulnerabilities: Bugs in the software code can serve as entry points for cybercriminals, emphasizing the importance of routine code audits.
Real-Time Data and Trends
Based on the Vietnam crypto stop movement and the data available from 2024, here are some statistics:
| Year | User Growth (%) | Reported Incidents |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 50 | 200 |
| 2022 | 120 | 500 |
| 2023 | 220 | 800 |
| 2024 | 300 | 1,200 |
Source: hibt.com
Future Trends in Blockchain Security
As we look to 2025 and beyond, here are some trends likely to shape the future of blockchain security:
- Increased Regulation: Governments are likely to impose stricter regulations, making security compliance standards essential.
- Rise of Decentralized Identity: Innovations surrounding decentralized identity frameworks may improve user privacy and security.
- Development of Quantum Resistant Algorithms: As quantum computing advances, the need for quantum-resistant blockchain algorithms becomes urgent.
In conclusion, as the Vietnam crypto stop movement gains momentum and more users enter the space, it’s essential to prioritize blockchain security. By adopting the necessary standards and being aware of past vulnerabilities, individuals and businesses can better protect their digital assets while navigating this exciting financial landscape.
For more information on cryptocurrency regulations, click to read our Vietnam crypto tax guide.
Stay secure in your crypto transactions and remember: Not financial advice. Always consult local regulators for guidance!
Written by Dr. Anh Nguyen, a blockchain technology expert with over 15 published papers and experience in auditing major crypto projects.